Abstract
In 2012, UN-Habitat launched the first State of Arab Cities report and conference — to address urbanization trends and challenges in the four major Arab and Middle Eastern regions: Mashreq, Maghreb, Gulf Cooperation Council, and the Southern Tier Countries (defined below). With Mona Serageldin as Team Leader, I2UD contributed a significant body of research for the conference, “Challenges of Urban Transition: Municipal Management and Urban Development Conference for Sustainability in Arab States.” The conference was hosted by the UN-Habitat Regional Office for Arab States (ROAS) and the Kuwait Knowledge Development Regional Centre.
The I2UD team compiled urban housing and demographic data for nations in Maghreb and Mashreq. The I2UD team reviewed 180 documents for each region, covering: “Population and Urbanization;” “Growing Role of Economic Cities;” “Urban Development and Housing Conditions;” “Transportation and Mobility;” “Urban Environmental Challenges;” “Urban Governance Systems;” “Transnational Migration;” and “Emerging Urban Issues and Innovations.” Additional materials includes data on regional Water Security, Food Security, Energy Security, and Air Pollution.
Documents include I2UD’s inception report, progress report, a I2UD Board Meeting presentation on the project, and a Kuwaiti Conference presentation (from the “Municipal Management and Urban Development Conference for Sustainability in Arab States,” from Kuwait on May 7, 2012). The Final Report for UN-Habitat State of Arab Cities 2012 lays out urban development and migration issues for nations in Mashreq, Maghreb, the Gulf Cooperation Council, and the Southern Tier regions, including I2UD’s contributions.
Maghreb includes Algeria, Libya, Morocco and Tunisia; Mashreq includes Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Syria; the Gulf Cooperation Council includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates; the Southern Tier includes Comoros, Djibouti, Mauritania, Somalia, Sudan, and Yemen.
Excerpt
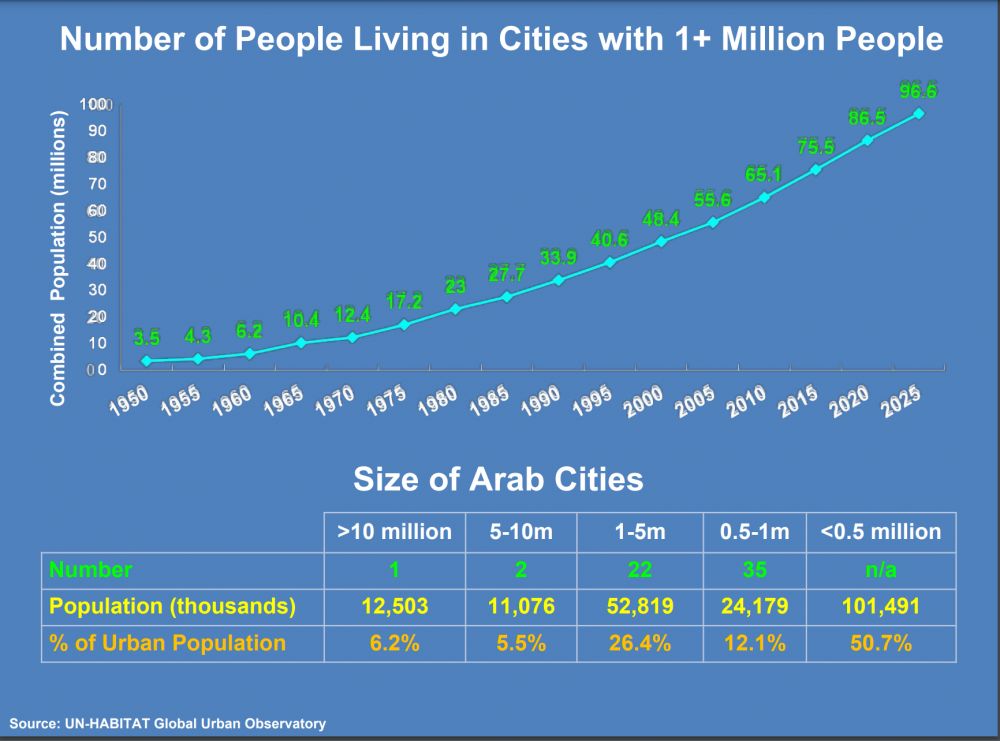
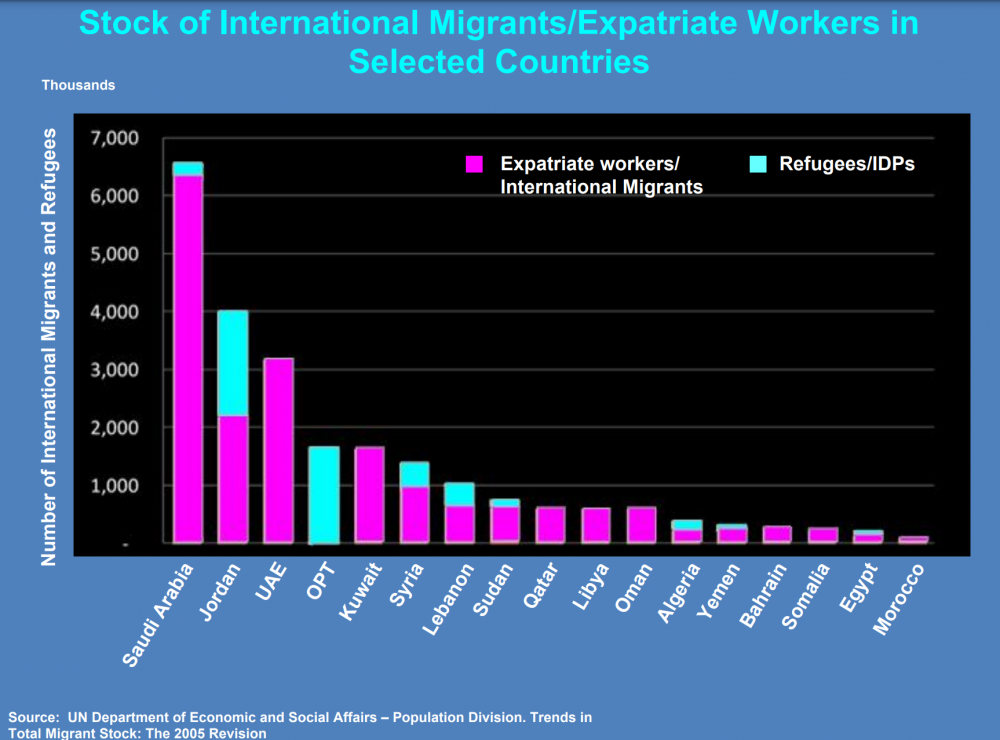
| Project Year: | 2010-2012 |
| Project Type: | Regional Report |
| Geographic Regions: | Middle East / North Africa |
| Reports: | State of Arab Cities: (Inception Report Presentation, November 2010) State of Arab Cities: (Progress Report Presentation, April 2011) State of Arab Cities: (Board Meeting Presentation, November 2011) State of Arab Cities: (Kuwait Conference Presentation, May 2012) State of Arab Cities: (Final Report, UN-Habitat, December 2012) |
| Authors: | François Vigier; Mona Serageldin; María-Luisa Fernández; Kendra Leith; Linda Shi |
| Sponsors: | UN-Habitat Regional Office for Arab States (ROAS) |
| Categories: | Urban Planning |
| ID: | 2010_07_001 |


