[Excerpt: 1984 Design Studio: Darb Al Ahmar District Medieval Cairo (Overview) 1.0 – Overview, page 80]
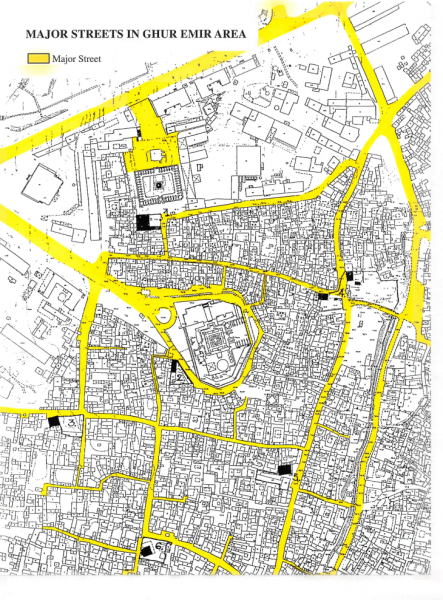
“The Darb al Ahmar district is located in the south-eastern portion of the medieval city, between al Azhar University (founded in 972) and Salah ed Din’s Citadel, the seat of government from the 12th century to 1865. It is bounded to the east by remnants of the medieval wall and to the west by Port Said Street, a wide avenue built over the antique canal connecting Cairo to the Red Sea. Its 4.8 km area is equal to roughly one quarter of the medieval city; its 1980 population was estimated at 148,000 or 23% of the medieval city’s population.
The district’s importance lies in its location; for nine hundred years it was the link between the institutions and commercial areas concentrated in the Fatimid City and the seat of government in the citadel. Since the 19th century, its western edge has been the dividing line between the modern, Europeanized city along the Nile and the indigenous urban pattern. Although the rapid expansion of Cairo after World War 1 led to its partial marginalization, this trend has been arrested and there is every indication that intensive development pressures are now at work, threatening the physical and social fabric of the area.”
“The diversity of Darb al Ahmar’s population reflects its long history. In the center, around what has been the main commercial artery since medieval times, a stable resident population working in trade and services is swelled daily by a growing number of students and rural migrants, particularly day laborers. Along the eastern edge, the historically less reputable quarters at the urban periphery are now outflanked by informal settlements spreading into the cemetaries and onto the top of the Makkatam hills. To the west, the boundary created by Port Said Street is no longer the sharp divider between foreign and indigenous population that it was in the colonial era. It is part of the transitional zone between the traditional and modern urban fabrics, leading to the key transport node of Ataba and the government district of Abdine. “
…
[Excerpt cont’ 1. 1 – Evolution of Darb al Ahmar, page 82]
“The northern half of the district, built as part of the Fatimid town, is bisected by the Qasabat, the main north-south street that runs from Bab al Fut’uh to Bab Zuweyla. Lined with shops serving the residential areas on either side of it, it is still today one of the major shopping streets in the medieval city. In the past, specialty shops were interspersed among the mosques, schools, baths, public fountains, and noble houses that lined the street. Bookstores and stationers were found near Al Azhar, inlaid copper articles were made and sold near the Ghuri mosque while, just off the main street, druggists were manufacturing herbal remedies. Just inside Bab Zuweyla, cooked-food vendors, a fruit market and sweetmeat sellers were to be found in the Suq es Sukkariya; musical instruments were also sold in a nearby market.”
The area outside Bah Zuweyla was first settled as a low density suburb, housing the spill-over population of the Fatimid city. It remained largely undeveloped until the beginning of the 12th century when a governmental edict mandated owners to develop their land or sell it to someone who would, under penalty of confiscation. The first public building built outside the wall, the al Saleh Tala’i mosque, opposite Bab Zuweyla, was completed in 1160. Development occurred along the wall, towards the Nile, and southward, along the two old roads to the old settlement of Fustat, which had continued to strive as a popular district after the official precinct had been moved north to al Qahira. By the end of the 12th century, development trends had been reinforced by the construction of a new fortified wall by Salah ed-Din, which increased the area of the city eight-fold, and by his moving the seat of government from the Fatimid city to a newly built citadel. Densities increased rapidly as commerces and craftsmen thrived along this strategic link between Cairo’s densest districts and the Citadel as two of Darb al Ahmar’s main streets the Tabbana and al Khyamiya provided the shortest route between Bab Zuweyla and Bab el Wazir, the city’s new southernmost gate at the foot of the Citadel. The areas behind these streets were progressively subdivided for residences, ranging in quality from palaces to tenements.”
Index: Darb al Ahmar District, Medieval Cairo, Egypt
1. Overview
– Table 5: Gross Residential Densities (c. 1976)
1.1 Evolution of Darb al Ahmar
1.2 Typology of Monuments
1.3 The Domestic Architecture
2. Transformations.
2.1 Evolution of the Physical Fabric
2.2 Social Change
– Household characteristics.
– Livelihood and income
– Housing conditions
3. Socio-Economic Indicators
3.1 Harah es Sokkariya
Cairo: Statistical Appendix.
Table of Contents:
1. Greater Cairo Housing Characteristics
2. Greater Cairo Employment Structures by Economic Activity
3. Medieval City – Demographic Characteristics
4. Medieval City – Education
5. Medieval City – Marital Status of the Adult Population
6. Medieval City – Household Size and Composition
7. Medieval City – Employment Status
8. Medieval City – Employment Structure by Economic Activity
9. Medieval City – Occupations
10. Medieval City – Commuting Patterns
11. Southern Sector Demographic Characteristics
12. Helwan District – Education
13. Helwan District – Marital Status
14. Helwan District – Household Size and Composition
15. Helwan District – Employment Status
16. Helwan District – Occupation
17. Helwan District – Characteristics of Housing Stock
18. Helwan District – Residential Densities
19. Helwan District – Commuting Patterns
[Excerpt: Darb al Ahmar, Overview: Bibliography, transcribed from hand-written text]
Nadim, Nawal (el Memiri). The Relationships between the sexes in a a Harah of Cairo, Indiana University, Doctoral Dissertation, 1975
Wikan, Unni, “Living conditions among Cairo’s poor – a View from Below, ” Middle East Journal, Vol. 39, No. 1, Winter, 1981(?), pp. 7-26.
Raymond, Andre, Artisans el Commercants au Caire au XVIIe siècle, Damascus; Institut Francais de Damascus, 1974. Tome I. Damas: Presses de l’Ifpo. doi:10.4000/books.ifpo.5950.
Revault, Jacques et Bernard Maury. Palais et maisons du Caire du XIVe au XVIIIe siècle, Le Caire : Institut Français d’Archéologie Orientale du Caire, 1975-79.
Ibrahim, Laila ‘Ali, “Residential Architecture in Mamluk Cairo,” in Mukarnas, Vol. 2, 1984.
Williams, John Allen, “Urbanization and Monument Construction in Mamluk Cairo,” in Makarnas, Vol. 2, 1984
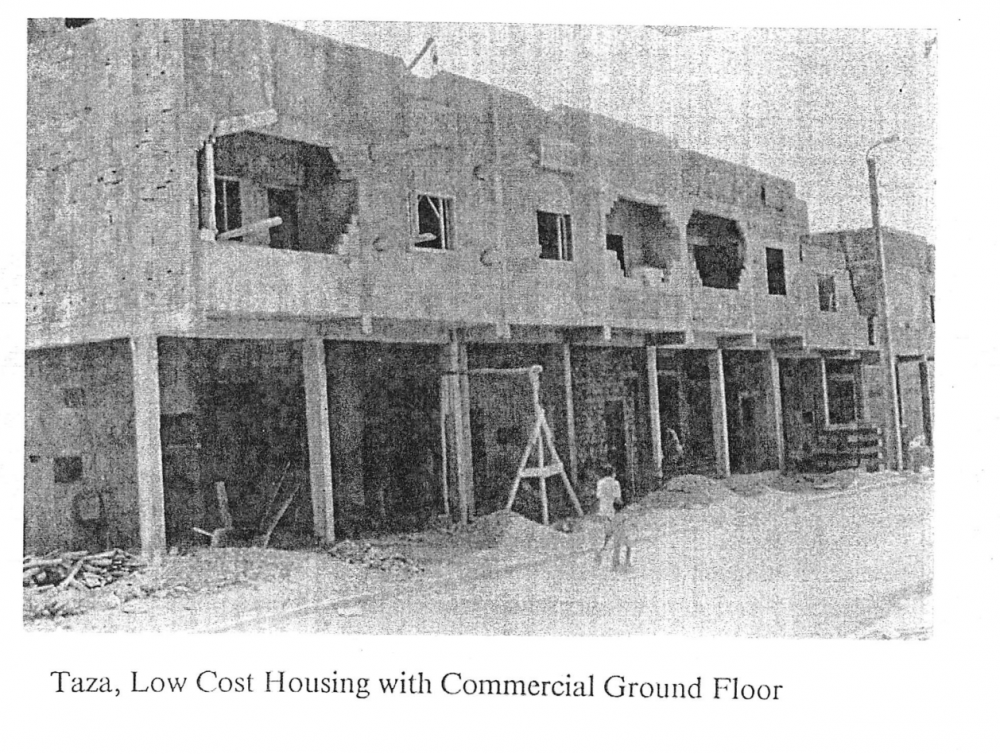







 Taza, Low Cost Housing with Commercial Ground Floor
Taza, Low Cost Housing with Commercial Ground Floor